We’ll go through what’s new in Bluetooth 5.3 and how it differs from prior versions, so you can see how much the new Bluetooth 5.3 innovates and improves on past versions. We’ll start with a list of Bluetooth versions and their new features, then go on to the differences and novelties that version 5.3 has to offer.
There are two things to keep in mind here. The first is that when two devices are connected over Bluetooth, the advances and innovations of the lower-version device are employed. As a result, connecting a Bluetooth 5.3 phone to a Bluetooth 5.2 speaker only gives you 5.2 improvements. Furthermore, each new version contains prior versions’ enhancements, so you won’t have to pick between the two; simply check for the most recent version on your future devices.
Bluetooth’s evolution, version by version
We’ll start with a list, which will show you all of the Bluetooth protocol’s previous versions as well as the major changes. Not only will you be able to observe the many versions and their release dates, but you will also be able to evaluate the relevance of each version’s innovations based on how much each of them has innovated.
Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology that allows you to connect computers, smartphones, tablets, and a variety of other linked devices such as watches, keyboards, mice, and speakers. All of this is accomplished without the usage of cables and using a secure radio frequency in the 2.4 GHz ISM band.
Bluetooth 1.0 was the original version, introduced in 1999, and it had a lot of connectivity and security issues because it was the first step in technology. It is presently out of service.
Bluetooth 1.1 was released in 2002 as the first update to Bluetooth 1.0. With a transmission rate of around 721 kbps, it is already a mature and commercial version.
Bluetooth 1.2 The second update to Bluetooth 1.0, released in 2003, eliminated the interference that remained in version 1.1, allowing the technology to be fine-tuned.
Bluetooth 2.0 was released in 2004, and it is backwards compatible with Bluetooth 1.2. The advent of the Enhanced Data Rate, which allowed it to deliver a transmission rate of a little over 2 Mb/s, was its most notable feature.
Bluetooth 2.1 was released in 2007, and it maintained the same transmission rate as the previous version. However, he offered a feature that revolutionised Bluetooth forever: the ability for one terminal to add to another and connect instantly without the need for a PIN or anything like that. It resulted in a significant increase in transmission rates, which may exceed 24 Mbps.
Bluetooth 4.0 This is arguably one of the most important versions of the standard, as it introduced Bluetooth Low Energy to offset the technology’s excessive battery usage. The 2010 version maintained a 24 Mb/s transfer rate and, due to its low power consumption, began to be employed on smaller and less powerful devices.
Released in 2013, it is notable for addressing the IoT (Internet of Things) environment, particularly by permitting direct connections between small devices.
Bluetooth 4.2 The following update, released in 2014, added the IPv6 protocol, allowing for direct Internet access.
In mid-2016, the big revolution arrived: a new stride forward that doubled the transfer rate, quadrupled the range, kept the IoT’s low-power philosophy alive, and allowed for more data in each transferred message. The transfer rate was up to 50 Mb/s, and the range was up to 240 metres in terms of numbers.
Bluetooth 5.1 A new version focused on location was released in 2019, allowing devices to know the location of other devices with whom they are connected to within centimetres. You’ll also be able to pinpoint the location of a signal that you’re looking for.
Bluetooth 5.2, also known as Bluetooth LE Audio, Bluetooth 5.2, also known as Bluetooth LE Audio, is a standard that enhances sound quality and energy efficiency on all devices that connect for audio tasks and was published in early 2020. It uses a new codec called the Low Complexity Communication Codec (LC3), which can compress and decompress data more quickly and allows music to be sent to several devices at once.
Bluetooth 5.3 was announced in July 2021, but it was not released until May 2022. Depending on the bandwidth necessary, this version offers lower consumption when utilised, less interference in the connections, better security in the connections, and better quality at all times. To keep polishing it, small details are necessary.
When comparing Bluetooth 5.3 to its predecessors, we may say that Bluetooth 5.0 is the foundation for the new Bluetooth protocol family. This is the most recent major update for Bluetooth 4, which doubled the file transfer rate and quadrupled the range (the distance at which they can communicate data to each other). The remainder of the iterations have merely improved minor details since then.
The focus of Bluetooth 5.1 is on locating devices, allowing them to know the location of other devices to which they are connected, and identifying the address from which their signal originates. Meanwhile, Bluetooth 5.2 focuses on sound, enhancing sound quality and reducing energy consumption in all devices that connect to audio services.
Bluetooth 5.3 is yet another minor update to the Bluetooth 5 family, this time focusing on improving energy economy and making connections less obtrusive. In addition, depending on the bandwidth required, it attempts to provide a greater safety level and better quality at all times.
This version has included a filter for updates to the periodic advertising process to increase performance by lowering energy use. This means that shipments remove data that is no longer needed, resulting in a minor reduction in energy usage during delivery.
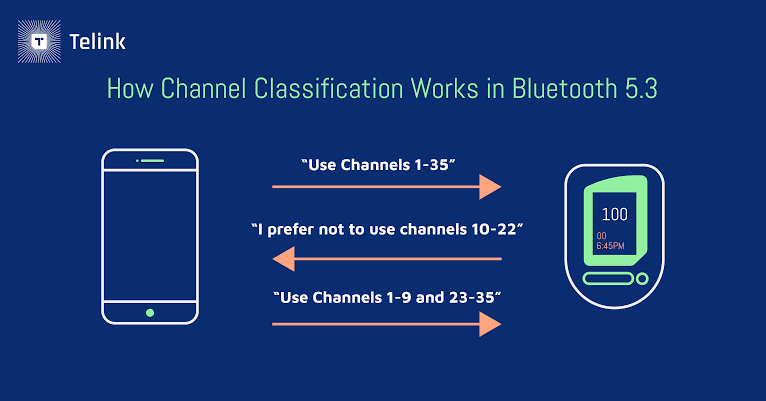
Furthermore, peripherals can specify a list of preferred channels so that the device that connects to them considers them and prioritises them over others. As a result, performance is enhanced and connection interference is reduced because the channels are not determined by a single device, such as a phone, but rather by them agreeing to use the lanes that best fit both of them.
Control over the size of the encryption key is improved in terms of security. This implies that the controller can now set a minimum key size, and if you connect to a device that isn’t very secure by using an encryption key that is too short, the connection will be dropped to protect you. Consumption is minimised as well, because the device only “fixes” those who match the requirements while connecting to them.
Finally, Bluetooth 5.3 allows your devices to select modes with increased bandwidth and minimal delay if appropriate. This means that if we use Bluetooth in a way that requires more bandwidth abruptly, such as switching from listening to music to making a phone call, the transition will be smoother.
There’s also an Intelligent Dual Bluetooth feature that lets you connect to two devices at the same time, both in standard mode and in BLE mode. This is a significant advancement because it will allow, for example, two mobile phones to connect through Bluetooth to a single speaker if all three devices are running version 5.3.
As a result, we can state that this version focuses on improving usage and privacy, all of which is done internally, so no configuration changes are required. However, the new Dual Smart Bluetooth capability is also incorporated, which can provide you with some intriguing new functionality.
What you need to know is that each new standard incorporates prior versions’ enhancements. This implies that when purchasing a device, you will not have to choose between the sound of 5.2 and the enhancements of 5.3; instead, look for the highest Bluetooth version available, as it will contain all of the additional capabilities that prior versions have implemented.